Table of contents
Introduction
SSH (Secure Shell) is a protocol that allows users to securely connect to remote servers and perform various tasks, such as executing commands and transferring files. One of the most common uses of SSH is connecting to a remote server via the command line. However, typing out the full command and credentials each time can be tedious and time-consuming. This is where SSH aliases come in.
An SSH alias is a shortcut that allows you to connect to a remote server using a simple command, rather than typing out the full command and credentials each time. This can be done using a config file, which is a file that contains all of your SSH connections and credentials. By creating an alias in this file, you can connect to a remote server with just one simple command.
Setting up the Config file
To set up an SSH alias, you first need to locate your SSH config file. This file is located in the .ssh directory in your home directory. The file is typically called config. If the file does not exist, you can create it.
Once you have located the config file, open it in a text editor. You can use any text editor you like, such as nano or vim. To create an alias, add the following lines to the file:
Host sftpdemo
HostName 34.125.54.210
User aditya
IdentityFile c:/Users/aditygupta/.ssh/gcp
The above credentials are to establish an SSH connection to a running Google Virtual Machine Instance. Here:
sftpdemois the alias.34.125.54.210is the external IP Address of the running VM instance.adityais the username.c:/Users/aditygupta/.ssh/gcpis the path of the private key file.
Other options such as Port can also be added as per your requirements.

Connecting to Virtual Machine
Once you have created your alias, you can connect to the virtual machine by running the following command:
ssh sftpdemo
Here's the result:
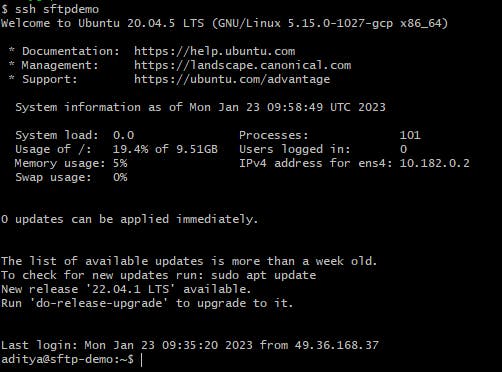
Now, we are connected to the remote server using the credentials and settings specified in the config file. You can also use this alias to perform other tasks, such as transferring files using SFTP.
Create an SFTP connection to the VM using the following command:
sftp sftpdemo
Once connected, we can transfer files from our local system to the VM securely.

Here, I've used the put command to upload wget.exe file from my local system to the bin folder in the VM Instance.
Tip: Windows users can run ssh and sftp commands using Git Bash.
In summary, SSH aliases allow you to connect to remote servers using a simple command, rather than typing out the full command and credentials each time. This can be done using a config file, which contains all of your SSH connections and credentials. By creating an alias in this file, you can connect to a remote server with just one simple command, making your work more efficient.
I hope this information was helpful and will make your work with SSH more efficient.

